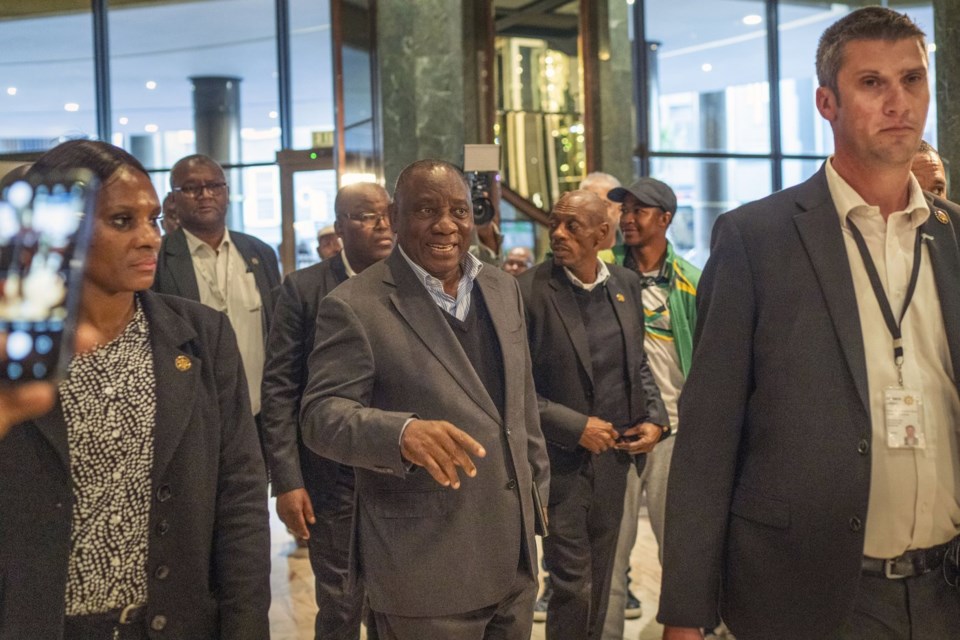
CAPE TOWN, South Africa (AP) — A top official with South Africa’s African National Congress party said Thursday it has a broad agreement with the main opposition and other parties to form a coalition government.
The announcement comes on the eve of the first sitting of South Africa’s new Parliament, when lawmakers will elect the president. The ANC needs help from other parties to reelect President Cyril Ramaphosa after it lost its long-held parliamentary majority in an election two weeks ago.
ANC Secretary-General Fikile Mbalula told reporters the main opposition Democratic Alliance and other smaller parties had agreed on the principle of forming a “government of national unity” with the ANC.
The ANC had a clear majority until this election since the end of the apartheid system of white minority rule in 1994 and a coalition government will be a first for South Africa at national level.
Lawmakers were expected to elect the country's president Friday after being sworn in at the first sitting of Parliament that will also reveal the kind of unity government the ruling African National Congress has cobbled together after losing its majority for the first time since 1994.
The lawmakers are also expected to elect Parliament's new speaker and deputy speaker, choices that will be determined by negotiations that have taken place between the ANC and opposition parties since the country's election results were declared nearly two weeks ago.
Parties are under pressure to conclude negotiations by Thursday to fulfill the constitutional requirement to swear in lawmakers and elect the president within 14 days of election results being declared.
The African National Congress won 40% of the national vote during the country's highly contested election, followed by the Democratic Alliance, or DA, with just over 21% and the newly formed uMkhonto weSizwe Party with about 15% of the vote in their first-ever election.
The ANC has opted to form a national unity government that will include most political parties that contested the election instead of a straightforward coalition with a few parties.
However, initial negotiations have laid bare the deep divisions between South Africa's political parties, with some already rejecting the proposed unity government while others have agreed to be part of it.
The ANC's national executive committee, the party's highest decision-making body between conferences, will meet in Cape Town on Thursday to finalize the agreements it has made with the other parties and will make an announcement afterwards.
On Wednesday, the Inkatha Freedom Party, the fifth-biggest party with 3.85% of the vote, confirmed it had decided to join the national unity government that will be led by the ANC.
It said it had also started negotiations to form a coalition with ANC and DA in the KwaZulu-Natal province where the MK Party got the most votes.
“We will participate in the government of national unity for the sake of our country and for the sake of our people, who want life to continue with a stable government that will address their challenges,” said IFP president Velenkosini Hlabisa.
While the MK Party emerged as arguably the biggest winner in the election with an impressive performance despite being formed only six months ago, it has refused to join the unity government and sought to prevent the sitting from going ahead.
Th Constitutional Court on Thursday dismissed the party's application to interdict the chief justice from convening the first sitting, giving a go-ahead for it to proceed.
The party continues to dispute the election results, claiming widespread vote-rigging, and has said its 58 elected lawmakers will boycott the sitting.
The South African Constitution says only one-third of Parliament’s 400 lawmakers need to be present for a quorum and for the vote to elect the president to proceed.
South Africa’s independent electoral commission and independent observers have declared the election free and fair.
As the deadline to reach an agreement approached on Thursday, the rift between DA and the fourth-biggest party, Economic Freedom Fighters, or EFF, appeared to be one of the main sticking points.
The leftist EFF has said that it won't be part of any arrangement that involves the centrist DA, which they accuse of being anti-Black and opposed to policies that aim to address the injustices of South Africa's past, including Black economic empowerment and land redistribution.
The parties remain ideologically at odds, with DA declaring the EFF its top rival last year.
The animosity between the two suggests the ANC might have to form a national unity government that doesn't include EFF and the MK Party, a pattern that may also play out in coalition governments at the provincial level, where the ANC also failed to maintain a majority in several provinces.
___
Magome reported from Johannesburg.
___
AP Africa news: https://apnews.com/hub/africa
Mogomotsi Magome And Gerald Imray, The Associated Press